Affiliate Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide to Getting Started and Succeeding

Affiliate marketing is a powerful and widely used strategy for earning passive income by promoting other people’s products or services. As one of the most popular ways to monetize websites, blogs, social media accounts, or YouTube channels, affiliate marketing enables individuals to earn commissions by promoting products they believe in. Whether you are an experienced marketer or just starting, understanding affiliate marketing’s basics, strategies, and best practices can help you succeed in this growing industry.
This article will explore the fundamentals of affiliate marketing, the various types of affiliate programs, and tips on how to succeed in this field.
1. What is Affiliate Marketing?
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based marketing strategy where businesses (merchants or advertisers) pay a commission to affiliates (partners) for generating sales, leads, or traffic to their website through the affiliate’s marketing efforts. Affiliates typically promote products or services through various online channels, such as blogs, social media platforms, email newsletters, or YouTube channels.
The affiliate is compensated for driving a desired action, which can be a purchase (CPA or Cost Per Action), a click (CPC or Cost Per Click), or a lead (CPL or Cost Per Lead). The commission is usually a percentage of the sale, but it can also be a flat fee, depending on the terms of the affiliate program.
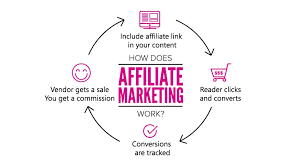
2. How Does Affiliate Marketing Work?
Affiliate marketing relies on a straightforward process involving three main parties:
- The Merchant/Advertiser: The business or company that creates and owns the product or service. The merchant typically runs the affiliate program and offers commissions to affiliates who promote their products or services.
- The Affiliate/Publisher: The individual or company that promotes the merchant’s products or services on their website, blog, or other online channels. The affiliate earns a commission for each sale, lead, or action generated through their promotional efforts.
- The Customer: The end-user who clicks on the affiliate’s link, makes a purchase, or completes an action (e.g., signing up for a newsletter or filling out a form). The customer doesn’t pay any additional fees to the affiliate, but their purchase or action triggers the affiliate’s commission.
The affiliate marketing process works as follows:
- The affiliate joins an affiliate program offered by a merchant or through an affiliate network.
- The affiliate receives a unique tracking link or referral code to promote the merchant’s product or service.
- The affiliate shares this link via content such as blog posts, YouTube videos, social media posts, or email marketing.
- When a customer clicks the affiliate link and completes the desired action (e.g., a purchase), the affiliate is credited for the referral.
- The affiliate earns a commission based on the agreed-upon terms, which is typically a percentage of the sale or a fixed amount for leads.
3. Types of Affiliate Marketing Programs
Affiliate programs come in various forms, and the right choice depends on the affiliate’s goals, audience, and marketing strategies. Below are the most common types of affiliate marketing programs:
3.1 Pay-Per-Sale (PPS)
This is the most common type of affiliate marketing model, where the affiliate earns a commission for each sale made through their affiliate link. The commission is usually a percentage of the product’s sale price.
- How It Works: When a customer clicks on the affiliate’s link and purchases the product, the affiliate receives a commission. For example, if an affiliate promotes a $100 product with a 10% commission, they would earn $10 per sale.
- Best For: Affiliates who want to promote products or services that are easy to sell and have a strong market demand.
3.2 Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
In the PPC model, affiliates earn a commission each time a customer clicks on their affiliate link, regardless of whether or not the customer makes a purchase.
- How It Works: Affiliates place ads or links on their website, blog, or other platforms. They are paid a small commission for each click, typically a few cents or dollars. If a customer clicks the link but does not buy anything, the affiliate still gets paid.
- Best For: Affiliates with a large audience or substantial traffic who are good at driving clicks, even if they do not always lead to sales.
3.3 Pay-Per-Lead (PPL)
With pay-per-lead affiliate programs, affiliates earn commissions when a referred customer performs a specific action such as filling out a form, signing up for a free trial, or subscribing to a newsletter.
- How It Works: Instead of a sale, the affiliate earns money when the referred customer provides their contact information, signs up for a trial, or completes another type of lead generation action.
- Best For: Affiliates targeting audiences in industries like finance, insurance, or education where customers often fill out forms to access more information or get a quote.
3.4 Recurring Commissions
In a recurring commission model, affiliates earn commissions on ongoing payments made by customers they refer. This model is commonly used for subscription-based products or services, such as SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms or membership programs.
- How It Works: Once an affiliate refers a customer who subscribes to a service, the affiliate continues to earn a commission as long as the customer remains subscribed. For example, if an affiliate refers a customer to a $50/month service with a 20% commission, they would earn $10 every month the customer remains subscribed.
- Best For: Affiliates who are promoting services or products with long-term subscription models and looking to build a steady stream of passive income.
4. Popular Affiliate Marketing Networks

There are numerous affiliate networks and platforms that connect affiliates with merchants. These networks simplify the process of finding affiliate programs to promote and provide tracking, payment, and reporting features. Some of the most popular affiliate marketing networks include:
- Amazon Associates: One of the largest and most well-known affiliate programs, offering affiliates the opportunity to promote a wide range of products across virtually every category.
- ClickBank: A leading platform for digital products like eBooks, software, and online courses. It offers a variety of affiliate programs with high commissions, particularly in niches like health, wellness, and personal development.
- CJ Affiliate (formerly Commission Junction): One of the largest and most established affiliate marketing networks, offering a variety of programs across multiple industries, including retail, finance, travel, and technology.
- Rakuten Marketing: A global affiliate network with a diverse range of merchants, particularly in retail, lifestyle, and technology.
- ShareASale: A well-known affiliate marketing platform with over 3,900 merchants across a range of industries, offering a variety of commission structures.
5. How to Get Started in Affiliate Marketing
Starting an affiliate marketing business requires strategic planning, effort, and a commitment to building your online presence. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to get started:
5.1 Choose Your Niche
Selecting a niche is one of the most important decisions you’ll make. The more specific and targeted your niche, the more likely you are to attract a loyal and engaged audience. Some common affiliate marketing niches include health and wellness, personal finance, technology, travel, fashion, and home improvement.
5.2 Research Affiliate Programs
After selecting a niche, research and join affiliate programs that align with your audience’s needs. Look for merchants offering quality products, good commissions, and reliable support. You can find affiliate programs directly through merchant websites, affiliate networks, or specialized platforms like ShareASale or ClickBank.
5.3 Create High-Quality Content
Content is king in affiliate marketing. To succeed, you must create valuable content that helps, educates, and engages your audience. This content can be in the form of blog posts, videos, product reviews, tutorials, or social media updates. Your content should provide honest and helpful recommendations to build trust with your audience.
5.4 Promote Affiliate Links
Once you’ve created your content, integrate your affiliate links strategically. Avoid overloading your content with links; instead, aim for natural, useful placements that make sense to the reader or viewer. Use call-to-action buttons, text links, banners, or affiliate links within your video descriptions.
5.5 Drive Traffic to Your Content
To generate sales and leads, you need traffic. Here are several ways to drive traffic to your affiliate content:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Optimize your content to rank higher in search engines like Google, making it easier for people to find your affiliate links.
- Social Media: Promote your content on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest to reach more people.
- Paid Ads: If you have a budget, consider running paid ads on Google, Facebook, or other platforms to drive targeted traffic.
- Email Marketing: Build an email list and send out newsletters promoting your affiliate content to a targeted audience.
5.6 Monitor Your Performance
Once your affiliate campaigns are live, it’s important to track performance. Monitor clicks, conversions, and commissions through the affiliate platform’s reporting tools. Based on the data, optimize your strategies by tweaking your content, testing different offers, and refining your marketing tactics.
6. Challenges in Affiliate Marketing
While affiliate marketing offers significant potential for income, it also comes with its own set of challenges:
- Competition: The affiliate marketing space is highly competitive, and standing out in a crowded market can be difficult.
- Traffic Generation: Driving consistent traffic to your website or affiliate links can take time, especially when starting from scratch.
- Compliance and Regulations: Affiliates must